In humans and animals many physiological processes are controlled by steroids, such as estrogen, testosterone, cortisol, etc. These steroids are important in reproduction, cardiovascular health, neurological functions and in general health. On the contrary, steroids are also implicated in the development and/or progression of many diseases, such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, endometrial cancer, liver cancer, colon cancer, osteoporosis, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular disease and obesity. Furthermore, oxidative metabolism of steroids has been shown to form toxic metabolites that can initiate the the disease processes andaffect general health.
Steroid Hormones Associated Diseases and Disorders
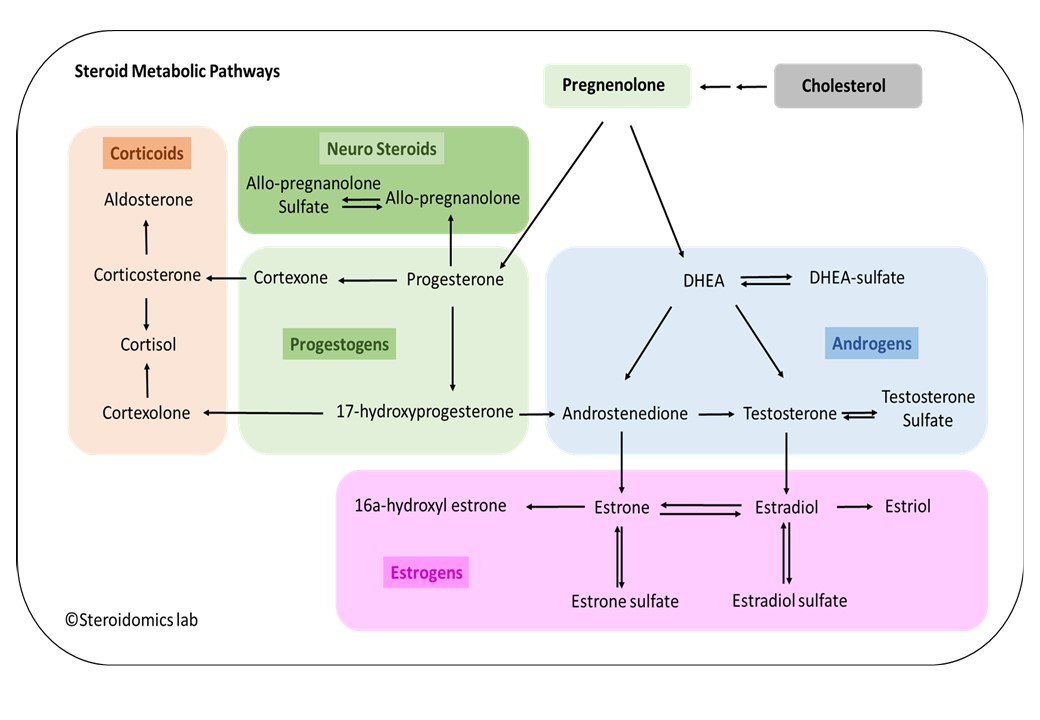
🧬 Steroid Hormones & Their Functions
Steroid hormones are lipid-soluble molecules derived from cholesterol. They easily cross cell membranes and bind to intracellular receptors, influencing gene expression.
1. Glucocorticoids
➡️ Primary hormone: Cortisol (produced in adrenal cortex – zona fasciculata)
✅ Physiological Functions:
- 🔄 Regulate metabolism: Stimulate gluconeogenesis, lipolysis, and protein breakdown
- 🧯 Anti-inflammatory effects: Suppress immune responses, inhibit prostaglandin/leukotriene synthesis
- 😰 Stress response: Increase blood glucose and blood pressure during stress
- 💦 Electrolyte balance: Mild mineralocorticoid activity (promotes sodium retention)
- 🧠 Mood & behavior modulation
2. Mineralocorticoids
➡️ Primary hormone: Aldosterone (produced in adrenal cortex – zona glomerulosa)
✅ Physiological Functions:
- 🧂 Regulates sodium and potassium balance
- Promotes Na⁺ reabsorption and K⁺/H⁺ excretion in the distal nephron
- 💧 Maintains blood pressure and extracellular fluid volume
3. Androgens
➡️ Primary hormone: Testosterone (males), DHEA/DHEAS (adrenal source)
✅ Physiological Functions:
- ♂️ Male sexual development: Promotes development of testes, penis, scrotum
- 💪 Muscle mass & strength: Stimulates protein synthesis
- 🧔 Secondary sex characteristics: Deep voice, facial/body hair
- 🧠 Libido and mood regulation
- 🦴 Bone growth and density
4. Estrogens
➡️ Primary hormone: Estradiol (E2)
✅ Physiological Functions:
- ♀️ Female sexual development: Maturation of uterus, vagina, and breasts
- ♻️ Menstrual cycle regulation: Stimulates endometrial proliferation
- 🦴 Bone maintenance: Inhibits bone resorption
- 🧠 Neuroprotective and mood-regulating
- ❤️ Cardiovascular health: Improves lipid profile (↑HDL, ↓LDL)
5. Progestogens
➡️ Primary hormone: Progesterone
✅ Physiological Functions:
- 🤰 Prepares uterus for implantation: Maintains endometrium after ovulation
- 🚫 Inhibits uterine contractions during pregnancy
- 🍼 Prepares breasts for lactation
- 🩸 Regulates menstrual cycle: Inhibits FSH and LH to prevent multiple ovulations
✅ Summary Chart
| Hormone | Key Functions |
| Cortisol | Metabolism, anti-inflammatory, stress response |
| Aldosterone | Na⁺ retention, K⁺/H⁺ excretion, BP control |
| Testosterone | Male development, muscle/bone growth, libido |
| Estrogens | Female development, menstrual cycle, bone health, cardiovascular protection |
| Progesterone | Uterine preparation, pregnancy maintenance, menstrual cycle regulation |