Neurosteroids are synthesized in brain as well as by endocrine gland. Regardless of their origin neurosteroids affect brain function, memory, learning, behavior through various pathways.
Neurosteroid Associated Diseases and Disorders
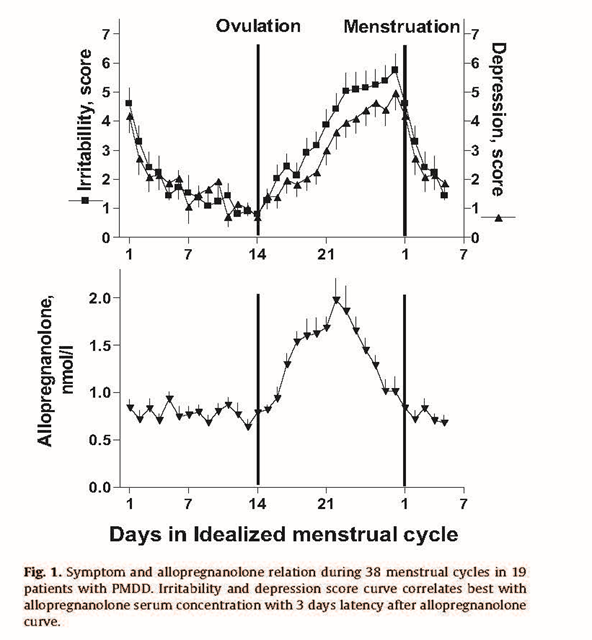
Allopregnanolone is a powerful neuroactive steroid derived from progesterone, and it plays a major role in brain function, mood regulation, and stress response. Here’s a complete overview of its physiological functions:
🧠 What Is Allopregnanolone?
- Allopregnanolone (3α,5α-tetrahydroprogesterone) is a neurosteroid.
- Synthesized in the central nervous system, adrenal glands, and gonads.
- Derived from progesterone through a series of enzymatic steps:
- Progesterone → 5α-DHP → Allopregnanolone
(via 5α-reductase and 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase)
- Progesterone → 5α-DHP → Allopregnanolone
⚙️ Physiological Functions of Allopregnanolone
1. 🧘♀️ GABA-A Receptor Modulation
- Acts as a positive allosteric modulator of GABA-A receptors (main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain).
- Enhances inhibitory signaling, leading to:
- Anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) effects
- Sedative/calming effects
- Anticonvulsant properties
- Neuroprotection
🧪 Mechanism is similar to benzodiazepines but via endogenous steroid signaling.
2. 😌 Mood Regulation
- Plays a key role in regulating mood and emotional resilience.
- Decreased allopregnanolone is linked to:
- Depression
- Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD)
- Postpartum depression (PPD)
3. 🧠 Stress Response
- Modulates the HPA axis (hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis).
- Helps control cortisol levels and buffers the effects of stress.
- Acts as a stress-adaptive neurosteroid, increasing during acute stress to calm the brain.
4. 🧬 Neurogenesis and Brain Plasticity
- Promotes the growth and survival of neurons, especially in the hippocampus.
- Important in learning, memory, and cognitive recovery after injury or trauma.
5. 🤰 Reproductive and Perinatal Roles
- Levels increase during pregnancy (especially in the 3rd trimester).
- Helps maintain calmness, sleep, and mood stability.
- May play a role in preparing the brain for maternal behavior.
6. 🌙 Sleep Regulation
- Supports slow-wave (deep) sleep and reduces sleep onset latency.
- Acts through its GABAergic effects to promote sedation.
📊 Summary Table
| Function | Effect |
| GABA-A modulation | Calming, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant |
| Mood stabilization | Protects against depression, PMDD, PPD |
| Stress regulation | Dampens cortisol and HPA axis |
| Neurogenesis | Promotes neuron survival and growth |
| Sleep promotion | Enhances deep sleep quality |
| Reproductive support | Supports emotional regulation during pregnancy |