Oxysterols play important roles in various biological processes such as cholesterol homeostasis, lipid metabolism, apoptosis. Oxysterols are associated with age-related diseases such as cardiovascular disease, eye disease (cataract, age related macular degeneration), neurodegenerative diseases, atherosclerosis and cancers.
Oxysterol Associated Diseases and Disorder
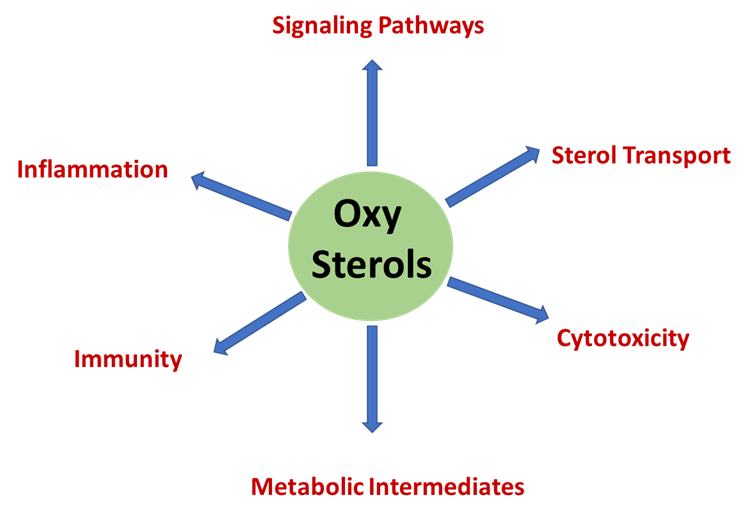
Physiological functions of oxysterols, the oxidized derivatives of cholesterol that act as crucial signaling molecules:
🧬 Oxysterols – Physiological Functions
Oxysterols are oxygenated forms of cholesterol, either enzymatically or non-enzymatically produced, with key roles in cholesterol homeostasis, immune response, and cell signaling.
✅ 1. Regulation of Cholesterol Homeostasis
- Oxysterols provide feedback inhibition of cholesterol synthesis:
- Inhibit HMG-CoA reductase (rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis)
- Suppress SREBP-2 activation, reducing cholesterol biosynthetic gene expression
✅ Key Oxysterols:
- 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol
- 25-hydroxycholesterol
- 27-hydroxycholesterol
✅ 2. Ligands for Nuclear Receptors (LXRs)
- Oxysterols are natural activators of Liver X Receptors (LXRα and LXRβ).
➡️ LXR activation leads to:
- Reverse cholesterol transport: ↑ABCA1, ABCG1 → promotes cholesterol efflux from cells
- Regulation of lipid metabolism: ↓cholesterol uptake, ↑cholesterol excretion
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Repress NF-κB-mediated cytokine production
✅ 3. Brain Cholesterol Turnover
- 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol is the major cholesterol excretion product from the brain.
- Helps maintain brain cholesterol balance, which is essential since cholesterol cannot cross the blood-brain barrier easily.
✅ 4. Immune System Modulation
- 25-hydroxycholesterol plays a key role in innate immunity:
- Inhibits viral replication (e.g., influenza, HIV, SARS-CoV-2)
- Regulates interferon-stimulated genes
- Modulates B cell function and antibody production
✅ 5. Bile Acid Synthesis
- Some oxysterols, like 27-hydroxycholesterol, serve as intermediates in bile acid synthesis in the liver via the alternative pathway.
✅ 6. Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Control
- Under certain conditions, oxysterols can:
- Induce cell cycle arrest
- Trigger apoptosis via oxidative stress mechanisms
🧾 Summary Table
| Function | Oxysterols Involved |
| Regulate cholesterol synthesis | 25-OHC, 27-OHC |
| Activate LXR and lipid metabolism | 24(S)-OHC, 27-OHC, 22(R)-OHC |
| Brain cholesterol turnover | 24(S)-OHC |
| Immune modulation & antiviral response | 25-OHC |
| Bile acid synthesis intermediate | 27-OHC |
| Apoptosis and redox signaling | 7-ketocholesterol, 7β-hydroxycholesterol |